
Radiata pine trees
Also known as Pinus radiata or the common name Monterey pine.
Location
Radiata pine is mostly grown in large plantations located on the Southern Slopes and Central Tablelands near Tumut and Bathurst, although it is also found in other areas of NSW. Smaller plantations are grown on the Northern tablelands near Walcha. Radiata pine was introduced to Australia from a small area near Monterey, on the West Coast of the USA. It is currently the most important single softwood species in the state.
Size
It grows up to 50 metres in height and 90 centimetres in diameter.
Identifying features
Radiata pine has a long straight cylindrical trunk. Its bark is dark reddish-brown, thick and deeply furrowed,with scaly ridges.
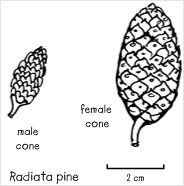
Radiata pine cones
Timber
Radiata pine is a softwood. It grows up to ten times faster than eucalypts. Its timber is creamy yellow, with distinct growth rings. The grain is straight and carpenters easily work it, making it a timber with low natural durablility.
Uses
The timber is particularly useful: it can be readily sawn for furniture production and house frames, peeled to make veneer and plywood, and pulped to make newsprint or pineboard. Your kitchen is probably from boards processed from Radiata pine. The bark is rich in tannins, which is suitable for the manufacture of adhesives.
If Radiata pine is treated with preservatives it is suitable for a long life in the ground or outside in the garden.
Did you know?
In its natural habitat, Radiata pine is not grown for timber production since it has poor form and slow growth, yet it grows well in other countries like Australia, New Zealand, Chile and Spain. Why do you think this is so?
For more information, see Radiata pine - the remarkable pine.
From cones to plantation:
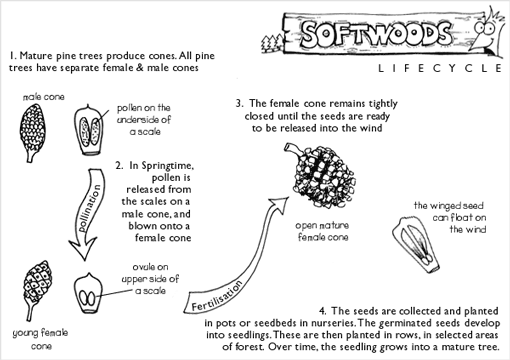
Radiata pine is a conifer or cone bearer. Conifers are trees which have cones and do not have flowers or fruit. Ripe (mature) pine cones from the best trees are selected by State Forests personnel for seed collection. The collected cones are heated and tumbled to release the seeds. The seeds are de-winged and sorted into size and weight before being planted into seedbeds or pots in a nursery. Fertilisers, fungicides and weeding is used to produce good seedlings. At about nine months old, the seedlings are ready for planting. A plantation is where many seedlings are planted by people and grown into trees for a range of purposes from timber production through to environmental protection.
How do the seeds get inside the cone?
Back to 'Supermodels' of state forests
