
A stand of spotted gums
Also known as Eucalyptus maculata or Corymbia maculata.
Location
Although spotted gum grows along the New South Wales coast and into southern Queensland, the highest value timber grows on the south coast of NSW, in sandy soils.
Size
It grows up to 50 metres in height and 1.4 metres in diameter.
Identifying features
The spotted gum is a tall, straight tree. It is easily recognised by its smooth, dimpled bark which is shed in summer, producing a mottled cream and grey 'spotted' appearance.
Note: The best way to identify the eucalypt species is to look around the base of the tree and discover the buds and fruits. The eucalypt flower develops into a woody capsule (fruit) after a few months. Each species has a fruit which has its own unique shape and features. The fruit is the single feature which most strongly identifies the species of eucalypt.
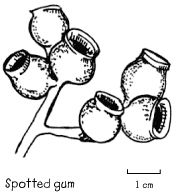
Woody capsules from the spotted gum
Timber
This is a native hardwood. The grain may be straight, wavy or interlocked. The wavy grain produces an attractive veneer.
Uses
This timber makes good tool handles because it is very strong, and is able to take shock. It can also be steam bent if a straight grain timber is chosen. Spotted gum is the main type of Australian timber used for tool handles which take high impact forces, like axe handles, because of these two important features.
These features make it ideal for heavy construction work in housing, piles, power poles, shipbuilding, weatherboards and flooring.
It is resistant to treatment with preservatives as it does not absorb them well. Spotted gum is also susceptible to borers.
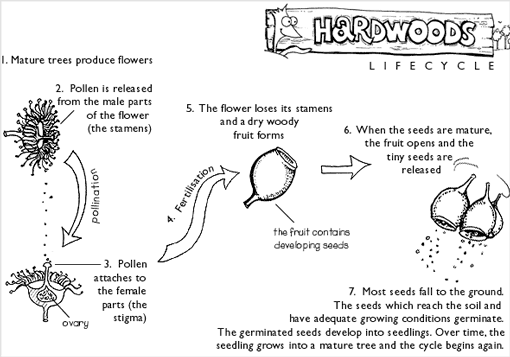
Where the seeds are found and how they're spread:
Back to 'Supermodels' of state forests
